Home>Resource >Samarium cobalt vs. neodymium iron boron
Samarium Cobalt vs. Neodymium Iron Boron
Deciding what material to use in your application can be challenging, especially when it comes to permanent magnet materials such as samarium cobalt and neodymium iron boron.
Determining whether or not to use Neo magnets instead of SmCo magnets in your high performance application is a function of:
- Maximum temperature of the application
- Required magnetic output at typical use temperature, and
- Total cost of the system.
Advantages of Samarium Cobalt:
- When compared to Neo, SmCo offers unique capabilities such as higher energy density at elevated temperatures.
- Maximum operating temperature for samarium cobalt is more than 2x neodymium iron boron.
- SmCo flux output varies much less with respect to temperature, meaning the device performance can truly be optimized.
SINTERED NEDOYMIUM MAGNETS
Our Rare-earth Nd-Fe-B magnet can be categorized into certain two types which are sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets and bonded Nd-Fe-B magnets. They are widely used in mobile phones, tablets, speakers, vibrating motors, voice coil motors, liner motors, manual sockets, computer accessories, etc., especially in magnetic assemblies (adding shunt, aluminum products, diaphragm, PSA, and AB glue).
We also have expertise in mass production automatically and manufacture our products in clean workplaces, in order to achieve best quality results.





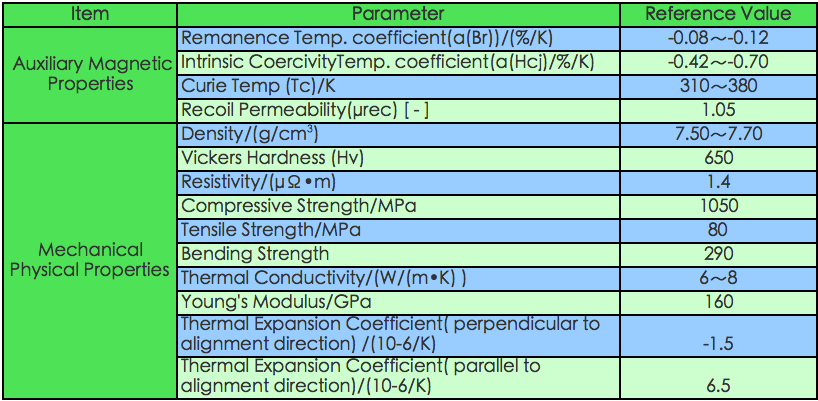
MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF SINTERED NEDOYMIUM MAGNETS
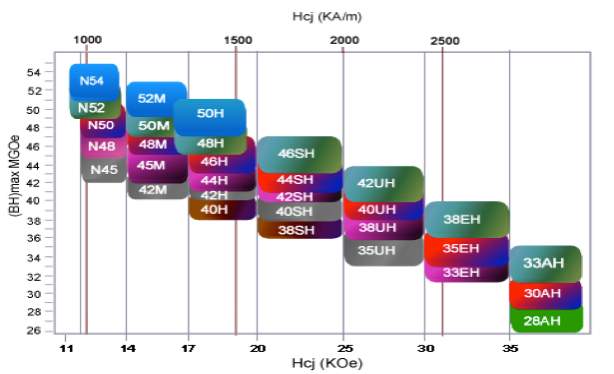
MAGNETIC PERFORMANCES
METHODS OF MAGNETIZATION

Radial Magnetised

Multi-poles Magnetised
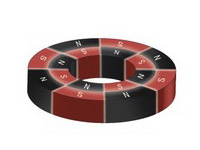
Multi-poles Magnetised Radial Orientation

Diametic Magnetised

Magnetised through its Heights

Axial Magnetised

Axial Magnetised Muli-poles

Single Surfax Multi-poles Magnetised

Sectors on One Surface Magnetised

Title-Type Maget-Radial Magnetised

Double Surface Multi-poles Magnetised

Title-type Magnet Diametic Magnetised
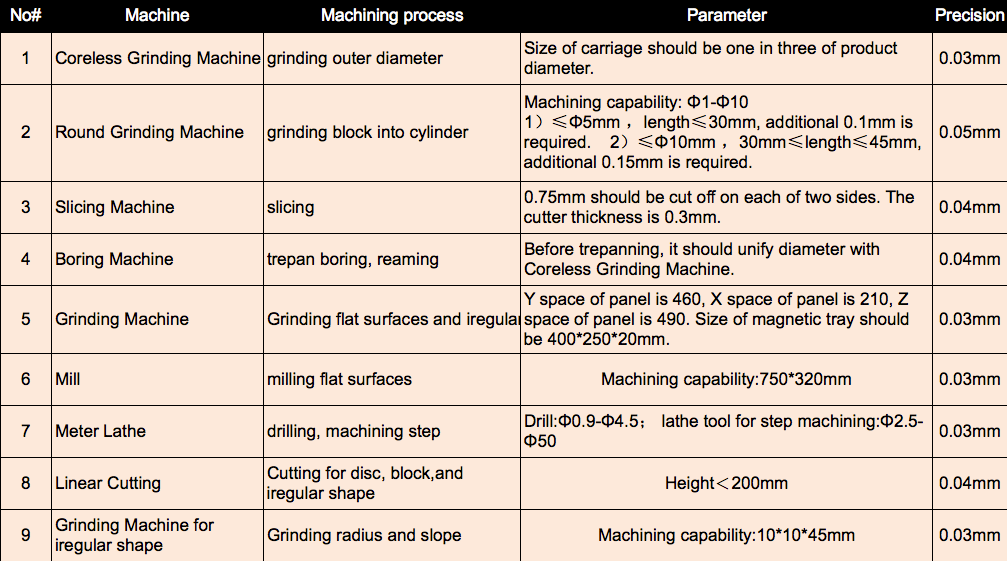
NEODYMIUM MAGNET MACHINING PROCESS